Affinity Dental Care – Oral Health
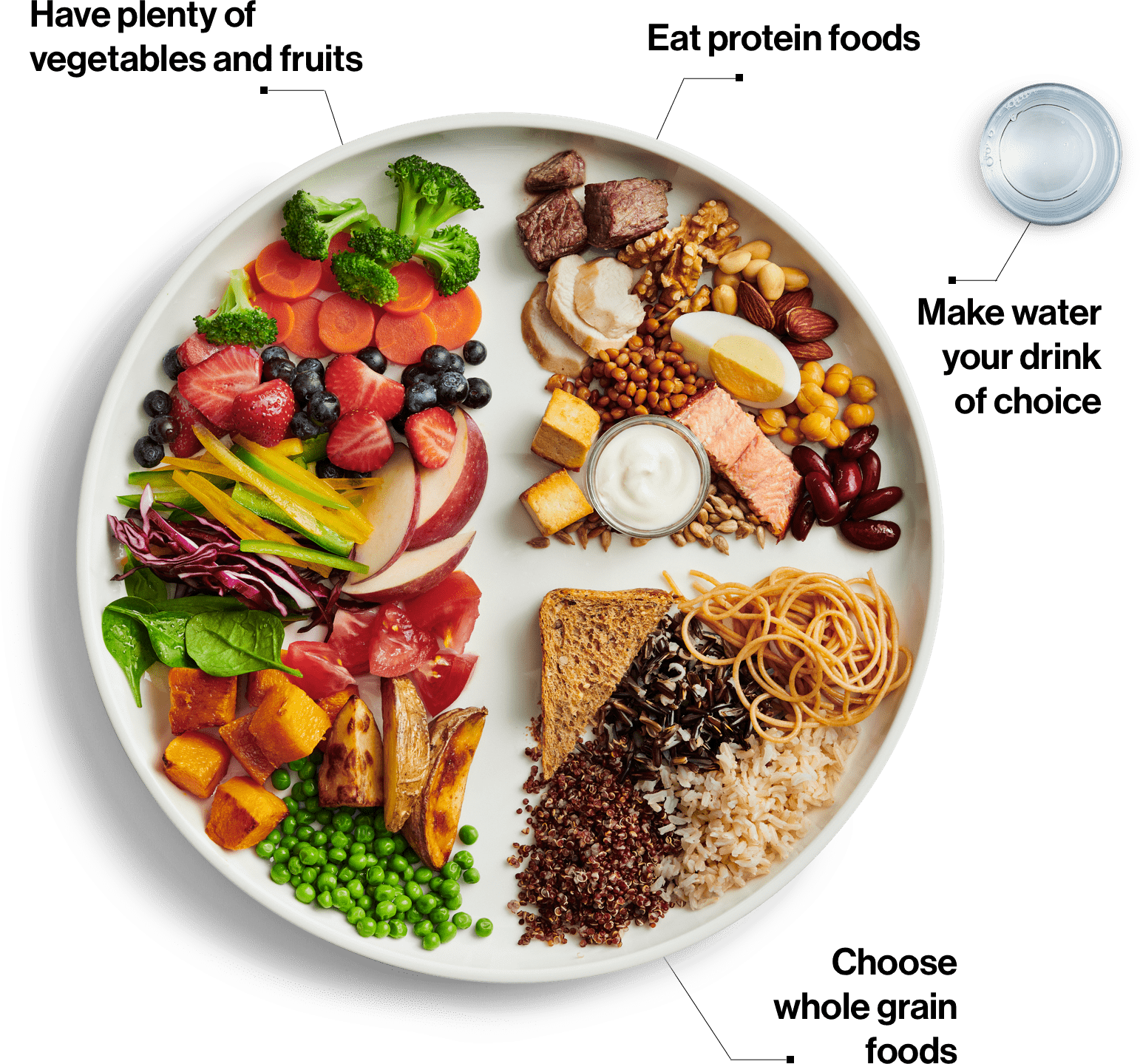
I have previously discussed nutrients and vitamins for oral health that can affect your wellness in several blogs. This time I would like to focus on oral and dental health. We all know that healthy eating will provide different nutrients for your wellness. A healthy balanced diet should contain a variety of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, fat-free dairy, and protein.
Vitamins A, B, C, D and minerals have significant oral health implications. Other nutrient intakes can also impact our oral and dental health. Let us look at them individually to see their impact on our oral health.
Vitamins for Oral Health:
Vitamins B, C, D, K & A
Vitamin B:
There are eight types of Vitamin B. Among them, Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin), B3 (Niacin), B6 (Pyridoxine), and B12 (Cyanocobalamin) are essential for our oral health. Deficiencies are most common in older adults, alcohol users, people with restricted diets, gastrointestinal issues or recent surgeries. Vitamin B complex deficiencies like Vitamin B2, 3, 6, and 12 can lead to recurrent aphthous stomatitis (canker sore), enamel hypo-mineralization, angular cheilitis (cracked mouth corners), halitosis (bad breath), gingivitis, glossitis (tongue inflammation), atrophy of the papillae, stomatitis (mouth ulcer), rashes around the nose, dysphagia (difficult swallowing), and pallor.
Vitamin C:
is also known as ascorbic acid. It is a water-soluble vitamin and is not stored in our bodies. It must be taken daily through food or supplements.
It controls infections and healing wounds and is a powerful antioxidant that can neutralize harmful free radicals. It is needed to make collagen, a fibrous protein in connective tissue vital for our various body systems in nerve, immune, bone, cartilage, ligament, blood, gums, and skin. A vitamin C deficiency can result in scurvy, resulting in bleeding gums and loose teeth.
A clinical trial conducted by Shimabukuro and colleagues on patients with gingivitis found that using Vitamin C could reduce spontaneous bleeding and redness of the gum. Patients having chronic gingivitis, chronic periodontitis, and type 2 diabetes can benefit from Vitamin C. Vitamin C is an antioxidant capable of inhibiting the initiation of carcinogenesis, including oral cancers, and can help neutralize the transformation of cells. In addition, a high intake of vitamin C from natural sources (i.e., fruits and vegetables) was associated with a significantly lower risk of head and neck cancer. Thus, vitamin C is currently recommended as a therapeutic measure to minimize the initiation and progression of oral cancer.
Vitamin D:
stimulates calcium and phosphorus absorption in the intestines and kidneys. It supports the functions of calcium and phosphorus in remineralizing and strengthening teeth. In children between the ages of six and eleven, several studies in Canada and Sweden have concluded that there is a significant inverse relationship between vitamin D levels in the body and caries development.
The results are probably due to incomplete calcification of teeth and alveolar bone. The incomplete calcification of enamel is called enamel hypoplasia. It is characterized by deficient, pitted, and rough enamel surfaces. These deformities increase the chances of bacteria colonization on teeth and difficulties cleaning the teeth. Deficiency in it will cause a low calcium level in the blood; the bones mobilize calcium to level out the blood calcium, leading to an increased risk for osteoporosis and arthritis (in adults) or rickets (in kids).
Vitamin D also plays a role in activating antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) such as Cathelicidins and Defensins. The increase in those AMPs in the oral epithelial cells, salivary ducts, and saliva lyse (break down) the oral bacteria significantly, reducing caries. Adequate Vitamin D in serum increases calcium content in the saliva. A deficiency of vitamin D can decrease the salivary flow by 65%. Therefore, vitamin D regulates salivary flow rate and quality.
Vitamin K:
The body needs vitamin K to produce prothrombin, a protein and clotting factor important in blood clotting and bone metabolism.
Deficiency is rare, but, in severe cases, it can increase bleeding and predispose a person to oral candidiasis.
Vitamin A:
Apart from its role in healthy vision, it is a critical component required to maintain the mucosal membranes, salivary glands, and teeth.
Saliva helps break down food and also cleans bacteria from in between your teeth. Deficiency will result in xerostomia (dry mouth), taste sensitivity, tooth brittleness, salivary gland degeneration, and caries risk. A lower intake of vitamin A has been associated with decreased oral epithelial development, impaired tooth formation, enamel hypoplasia and periodontitis
Vitamins for Oral Health:
Calcium, Protein, Folic Acid, Zinc, Magnesium & Potassium
Calcium:
is the main components in the mineralization of the protein matrix of bone and teeth. The hardened substance made up of the two minerals is called hydroxyapatite. It gives bones and teeth their compressive strength. Inadequate absorption during pregnancy may result in bone deformities, incomplete tooth calcification, tooth malformation, and increased susceptibility to caries after tooth eruption.
In adolescence, inadequate intake of calcium will lead to osteopenia or osteoporosis.
Protein:
is needed to construct all body tissues and is a fundamental building block for any living organism. Protein deficiency results in the poor structural integrity of the dentition and the supporting periodontal tissues. Delayed wound healing and poor resistance to oral pathogens.
Folic acid:
is the synthetic form of vitamin B9, also known as pteroylmonoglutamic acid. Folate is the naturally occurring form of vitamin B9. It is essential for DNA synthesis. Deficiency in folate during pregnancy can lead to cleft lip or palate. Lack of it can lead to angular cheilitis, stomatitis, sore or burning mouth, inflamed gingiva, and glossitis.
Zinc:
is often found in oral rinses and toothpaste because it helps with common gum diseases, including gingivitis and other common periodontal problems.
Low zinc levels can increase the chance of developing infections and degenerative pathologies. Zinc also plays a vital role in the psychosocial functioning of human behaviour. In the oral cavity, zinc is found in saliva, dental plaque, and enamel. It contributes to healthy teeth formation and the reduction of halitosis in the mouth
Clinical trials have demonstrated that zinc ions decrease the rate of enamel demineralization.
Magnesium:
Magnesium and calcium complement each other to build hard tooth enamel and maintain bone density. Ideally, you should receive a two-to-one ratio of calcium to magnesium daily. Good dietary sources of magnesium include dark green vegetables, legumes, nuts, corn, brown rice, buckwheat, rye, and other whole grains. Too much magnesium all at once can cause digestive side effects such as diarrhea, so you may need to spread your intake out over the day.
Potassium:
A diet rich in Potassium can help your teeth and bones use calcium more efficiently because Potassium is a companion to magnesium in the body’s efforts to regulate blood acidity. When your blood becomes too acidic, the acids can remove calcium from your teeth and jawbone, weakening them.
You can get Potassium from many foods. Bananas, prunes, avocados, potatoes (including sweet potatoes), tomatoes, and Swiss chard are all rich in Potassium.
Potassium nitrate is also found in some toothpaste to help to reduce tooth sensitivity.
Affinity Dental Care is a general dental clinic in Burlington that provides comprehensive treatment for the families in the neighbourhood. If you are looking for an excellent dental clinic near you, please call 289-861-5111 or email us at info@affinitydentalcare.ca for a consultation on your dental health status.